What is Thermodynamics?
Thermodynamics is the study of heat, work, and energy transfer in systems. Its key principles include:
- First Law: Energy is conserved; it can be transformed but not created or destroyed.
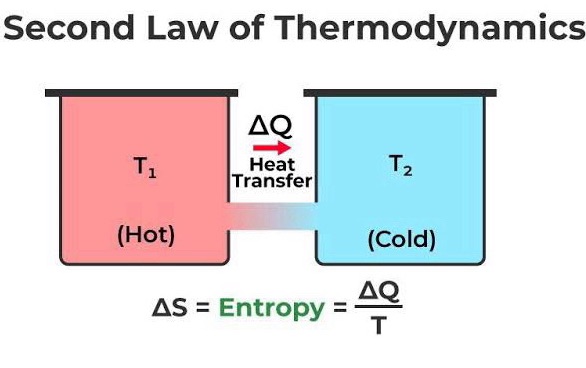
- Second Law: Entropy (disorder) always increases in isolated systems, dictating the direction of natural processes.
- Third Law: As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero.
- Zeroth Law: Systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in equilibrium with each other, defining temperature.
It applies to various scientific and engineering fields to understand energy processes.
Why is it Proven?
Thermodynamics is proven through:
- Empirical Observations: Real-world systems, like engines and refrigerators, consistently align with thermodynamic principles.
- Heat Engines: The performance and efficiency of heat engines match theoretical predictions.
- Thermodynamic Cycles: Predictable patterns in engine cycles validate thermodynamic laws.
- Experimental Verification: Experiments measuring heat, work, and energy changes confirm the laws of thermodynamics.
- Statistical Mechanics: Links microscopic behavior to macroscopic thermodynamic properties, supporting the laws.
- Specific Heat Capacities: Measurements of heat required for temperature changes match predictions.
- Phase Changes: Observed behavior during phase transitions confirms thermodynamic principles.
- Entropy and Irreversibility: The natural increase in entropy aligns with theoretical predictions about irreversible processes.
- Practical Applications: Successful technologies like refrigeration and air conditioning demonstrate the laws in action.